The number of fatal cancer diagnoses being reported started to skyrocket in early 2021.
Most of the cases are being dubbed “turbo cancers” due to the rapid onset and development of the disease, which doctors say is a new phenomenon that was unheard of three years ago
However, medical professionals and health officials say they are “baffled” about what could be causing the spike.
Nearly every continent is experiencing an increase in various types of cancer in people under 50 years old, which is particularly problematic as the disease tends to be caught in later stages in this population because most doctors aren’t trained to look for it in young people.
The disparities in rates and types of the disease are puzzling scientists and have prompted some to kick off multi-decade research projects that will involve hundreds of thousands of people from around the world.
Globally, Australia has seen the highest number of early-onset cancer diagnoses in the world, with a rate of 135 per 100,000 people.
Nearby New Zealand has the second highest rate, at 119 cases in people under 50 per 100,000 people.
But while breast cancer is the top disease in Australia, colon cancer ranks first in its neighbor.
In Asia, Japan and South Korea may be close in proximity and similar economically, but they have different rates of early-onset colon cancer, which is increasing at a faster rate in South Korea.
The United States falls in sixth place, with 87 cases per 100,000 people under 50 years old and the U.K. takes the 28th spot, with 70.5 cases per 100,000 people.
Cancers increasing the fastest include throat and prostate cancers. Early-onset cancers with the highest mortality include beast, tracheal (windpipe), lung, stomach and colon.
Experts have long speculated the increasing obesity rates and earlier cancer screenings may be behind the rise, as well as high-fat diets, alcohol consumption, and tobacco use.
However, because lifestyles, habits, and diets vary so widely from country to country, they now believe these factors do not entirely account for the surge.
Daniel Huang, a hepatologist at the National University of Singapore, told Nature:
“Many have hypothesized that things like obesity and alcohol consumption might explain some of our findings.
“But it looks like you need a deeper dive into the data.”
More recent researchers have begun to focus on a genetic component of early-onset cancer. Some have found younger people develop more aggressive tumors than older patients, which are better at suppressing a person’s immune system.
Pathologist Shuji Ogino at Harvard Medical School and his colleagues have also discovered a weakened immune response in people with early-onset tumors.
Still, however, the differences are subtle, Ogino said, and a clear reason cannot be determined.
According to the news article in Nature, the rates of some cancers in some countries were increasing before 2020.
For example: “In the United States, where data on cancer incidence is particularly rigorous, uterine cancer has increased by 2% each year since the mid-1990s among adults younger than 50
Early-onset breast cancer increased by 3.8% per year between 2016 and 2019.”
However, recent trends indicate a surge since the pandemic that researchers think is set to continue for a number of years:
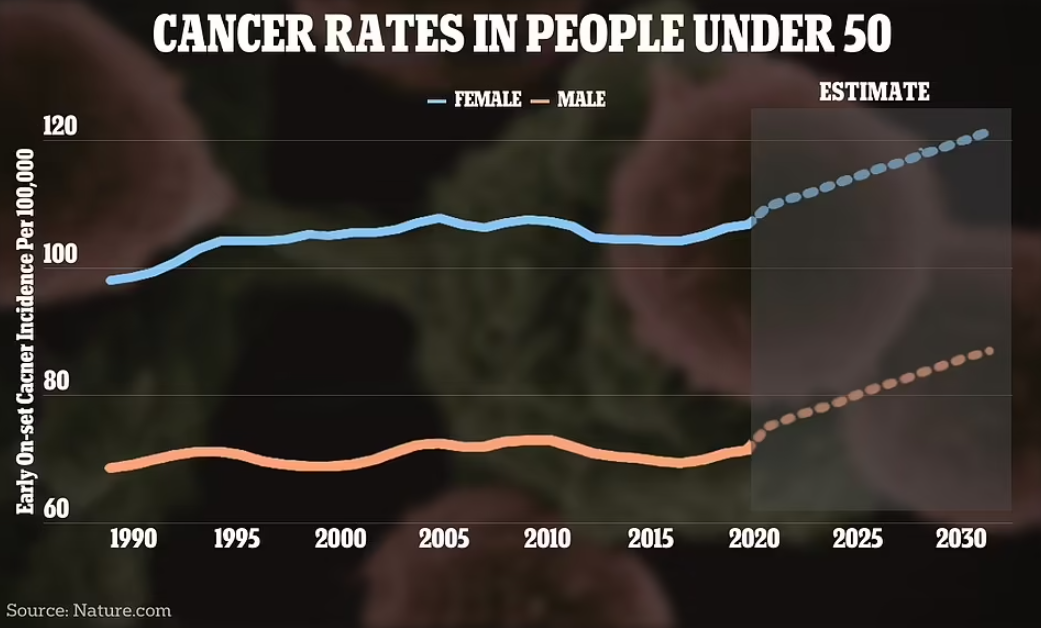
Statistics from around the world are now clear: the rates of more than a dozen cancers are increasing among adults under the age of 50.
This rise varies from country to country and cancer to cancer, but models based on global data predict that the number of early-onset cancer cases will increase by around 30% between 2019 and 2030
The chart showing this predicted surge in overall cancer rates is shown below:
So what could be causing this “mysterious” deadly spike?

No comments:
Post a Comment